√画像をダウンロード gravitational potential energy roller coaster examples 118558-Gravitational potential energy roller coaster examples
For example, if a 0500kg mass hung from a cuckoo clock is raised 100 m, then its change in gravitational potential energy is latex\begin{array}{lll}mgh&=&(0500\text{ kg})(980\text{ m/s}^2)(100\text{ m})\\\text{ }&=&490\text{ kg}\cdot\text{m}^2\text{/s}^2=490\text{ J}\end{array}\\/latexMar 01, 14 · Roller Coasters The main energy transfers that happens as a "car" travels along the track from the start of the ride to the end 1 The main energy transfers are between gravitational potential energy (GPE) and kinetic energy (KE), and the eventual decrease of mechanical energy as it transforms into thermal energyFor example, a roller coaster car possesses increasing gravitational potential energy as it is raised higher and higher along a track, due to the earth's gravitational field For most roller coasters, the gravitational potential energy of the cars at the peak of the first hill
Gravitational Potential Energy Physics
Gravitational potential energy roller coaster examples
Gravitational potential energy roller coaster examples-The roller coaster car and children experience the greatest gravitational potential energy when they are located at the top of the first hill As the roller coaster car goes down Hill 1, the amount of kinetic energyGive three examples of objects that have potential energy 1A roller coaster at the top of a hill 2A bow and arrow when it is being pulled back before you shoot it 3A windup toy when The reason a roller coaster has gravitational energy is because as the roller coaster comes to the top of a loop or a hill it uses gravitational energy to



Q Tbn And9gcrafefy3jl Oxipbbpqgr5txanp77t8w Sjgfnczxnintwi9klx Usqp Cau
Potential Energy is defined as stored energy 4 Give an example of an object that would have gravitational potential energy 5 A roller coaster sits at rest at the top of a meter hill (No calculations needed) a What is true about the potential energy of the roller coaster?A roller coaster ride at an amusement park starts from rest at a height of 50 m above the ground and rapidly drops down along its track At some point, the track does a full 360° loop which has a height of m, before finishing off at ground level The roller coasterGravitational Potential Energy Roller coasters store gravitational potential energy(GPE) at the top of each hill, which basically means gravity is the force that gives the coaster the energy to move down the hill and back up again There are several examples of GPE such as holding a basketball in your hands, a piece of gum in your mouth, a phone in your pocket, or your tray of
Work and Energy Gravitational Potential Energy Level 2, Example 2 Starting from rest at point A, a 350kg roller coaster car slides along the frictionlessNov , · For instance, a car parked at the top of a hill is an example of mechanical gravitational potential energy since the automobile has the potential to come down the hill It's the same with a roller coaster that halts at the highest point of the rails 5Questions scaffolded to analyze a roller coaster simulation finding the points of greatest and least potential and kinetic energy using an online roller coaster simulation, a chart, and questions This addresses 8th grade Physical Science TEKS 68a Compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy
Between Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy is the Roller Coaster!Nov 14, 19 · Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object has stored because of its mass and its height off the ground Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its mass and its velocityMESA Notebooks Example definition stored energy In the case of roller coasters, it is gravitational potential energy, energy that an object has by virtue of its position in a gravitational field (ie if the object is some height above the ground, it has the potential to fall to the ground because gravity is pulling on it)




Identify Where Potential Energy Is Least Or Greatest As An Object Changes Position Middle School Physical Science




Gravitational Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
Example Potential energy changes for a roller coaster A 1000kg rollercoaster car moves from point 1 to point 2 and then to point 3 (a) What is the gravitational potential energy at points 2 and 3We are going to build roller coasters!Gravitational potential energy is the energy in an object because vertical position or height Gravitational attraction of the Earth is why the energy is stored Examples of items that elastic potential energy can be stored in include rubber bands, bungee cords, trampolines, springs, an arrow drawn into a bow In Roller Coasters gravity




Gravitational Potential Energy By Lissan Aklog




Imathas Libretexts Assessment
Gravitational energy is the potential energy associated with gravitational force (a conservative force), as work is required to elevate objects against Earth's gravity The potential energy due to elevated positions is called gravitational potential energy, evidenced, for example, by water held in an elevated reservoir or behind a dam (as anThis first hill of a roller coaster is normally the tallest Once the cars are pulled to the top of the hill, they maintain gravitational potential energy The first hill maintains the largest amount of potential energy Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational fieldGravitational potential energy is energy stored in an object due to height The value of PE G is directly related to and depends on height Thus, if height doubles, the gravitational potential



Potential Vs Kinetic Energy Lessons Blendspace




How Rollercoasters Work Science Of Rollercoasters
Let W be the gravitational potential energy at the top of the hill Then, where m is the mass of the roller coaster, and g is the acceleration due to gravity, which equals 98 m/s 2 on earth's surface The kinetic energy of the roller coaster is where v is the speed of the roller coaster If we assume no friction losses, then energy is conservedA roller coaster ride, unlike a yoyo, actually allows a person to feel the tangible effect of energy transfers between potential and kinetic energy For example, when ascending the first hill of a roller coaster, the train gradually builds potential energy until it reaches the very top At the very top, riders can feel a tiny moment of stillness, and this moment is the point where the coaster has reached its maximum potential energy, and all of its energyA compressed spring A monkey increases its gravitational potential energy by climbing to the top of the tree What happens to that potential energy if he climbs back down halfway?




Speed Stopping Distance Of A Roller Coaster Physics University Of Wisconsin Green Bay



Rollercoaster
The maximum kinetic energy generated is when the roller coaster is at the bottom of the track When it begins to go up, the kinetic energy converts to potential energy Floating at the funfair!May 07, · In roller coasters, the two forms of energy that are most important are gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy Gravitational potential energy is the energy that an object has because of its height and is equal to the object's mass multiplied by its height multiplied by the gravitational constant (PE = mgh)Jul 16, · For example, if a 0500kg mass hung from a cuckoo clock is raised 100 m, then its change in gravitational potential energy is mgh = (0500kg)(980m / s2)(100m) = 490kg ⋅ m2 / s2 = 490J Note that the units of gravitational potential energy turn out to be joules, the same as for work and other forms of energy



Newton S Laws At Work Joule S Experiment On Heat And The Gravitational Potential Energy In The Earth S Field Steemit




A Frictionless Roller Coaster Of Mass M 5 Kg Tops The First Hill With Study Com
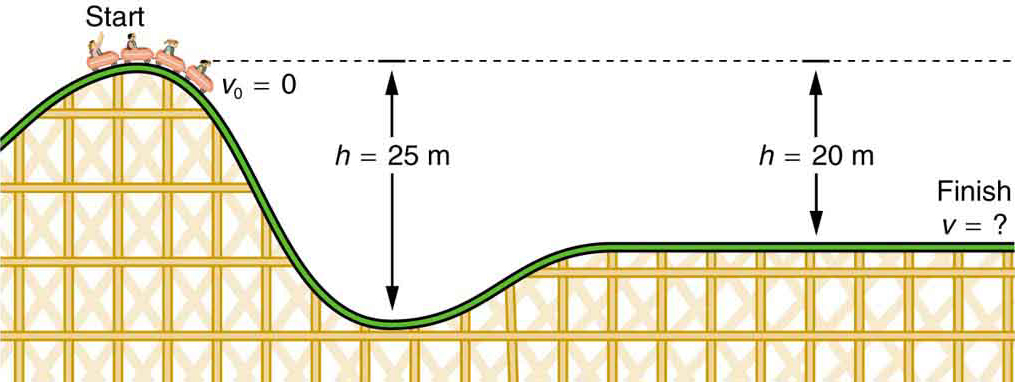
Gravitational Potential Energy Roller coasters store gravitational potential energy(GPE) at the top of each hill, which basically means gravity is the force that gives the coaster the energy to move down the hill and back up again There are several examples of GPE such as holding a basketball in your hands, a piece of gum in your mouth, a phone in your pocket, or your tray ofThink back to the roller coaster example in the introduction Initially, the roller coaster is given a large amount of gravitational potential energy as it is pulled to the top of a very tall hill What happens to that potential energy as the roller coaster continues down the hill?Viewed in terms of energy, the rollercoasterEarth system's gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy If work done by friction is negligible, all ΔPE g is converted to KE Strategy The roller coaster loses potential energy as it goes downhill




Potential Energy Wikipedia




Potential And Kinetic Energy Forms Stored Chemical Mechanical Nuclear Gravitational Gravity Elementary Energy Lesson Science
Roller coasters are paradise for many thrill seekers Roller coasters rely on conservation of energy Whether you are riding a modern roller coaster or a roller coaster from generations ago, the basic design principles remain the same On a Roller coaster energy changes from potential to kinetic and back again many times over the course of a rideFocus on other examples of gravitational potential energy due to arrangement of objects interacting at a distance, both close to surface of Earth like roller coaster and farther in space Examples asteroid falling to impact Earth and resultingRoller Coasters are an excellent example of energy conservation at work (and play) Each group will build a roller coaster (using a marble or steel ball as the rider) out of materials of their choice (discussed below)




Pin On Energy




Where Is The Motor On A Roller Coaster Google Search
Jan 23, 12 · Potential energy is a property of a system rather than of a single object—due to its physical position An object's gravitational potential is due to its position relative to the surroundings within the Earthobject system The force applied to the object is an external force, from outside the system When it does positive work it increasesSep 05, 07 · The roller coaster is a great example of conversions between potential energy (stored energy) and kinetic energy (the energy of motion) As the cars are being pulled up to the top of the first hill, they are acquiring potential energy The chain that pulls them up the hill works against the force of gravityIn this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have Joules of potential energy, PE = 3kg * 981 m/s 2 * 5m = J 981 meters per second squared (or more accurately m/s 2 ) is widely accepted among scientists as a working average value for Earth's gravitational pull




How Do Roller Coasters Work Wonderopolis




What Is The Difference Between Potential And Kinetic Energy
Dec 15, 16 · The law of conservation of energy states that energy can not be created or destroyed Therefore, other than the force transferred externally as a result of friction as heat, all the energy is still conserved In a roller coaster, the only two types energy involved, gravitational potential energy and kinetic energyIt has potential energy bGravity, potential and kinetic energy, and friction are all considered when making roller coasters This makes them a great activity for students to learn about physics You can use the Pitsco Roller Coaster Track Stands Package and Roller Coaster Track to build roller coasters in your classroom, but first, let's take a closer look at roller coasters When you look at a roller coaster,




Ks3 Y9 Physics Kinetic Energy Teaching Resources




Ak Lectures Potential And Kinetic Energy On Roller Coaster
Potential energy examplesIn this video, I show examples of potential energyPotential energy is stored energyI give examples of gravitational potential energMar 27, · In roller coasters, the two forms of energy that are most important are gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy Gravitational potential energy is the energy that an object has because of its height and is equal to the object's mass multiplied by its height multiplied by the gravitational constant (PE = mgh)Nov 03, 18 · Roller coasters are an excellent way to teach your students about conservation of energy Gravitational* potential energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its height off the ground Kinetic energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its mass and its speed When a roller coaster car reaches the top of its very




Ak Lectures Potential And Kinetic Energy On Roller Coaster




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics
Feb 19, 16 · Gravitational potential energy depends on an object's weight and its height above the ground Other Forms of Potential Energy All of the examples of potential energy described above involve movement or the potential to move The form of energy that involves movement is called mechanical energyA roller coaster is a great example of gravitational potential energy changing to kinetic energy Potential energy can come in many forms For example, chemical energy can be stored and later converted into heat or electricity show more content Friction plays a major role in actual roller coaster physics Once cars are lifted to the topThe height data correlates with the potential energy Students can also indicate where the marble has most kinetic energy (where it is also losing the most PE) Background information on real roller coasters A real roller coaster has no engine and once elevated to its start point is entirely driven by the force of gravity




Physical Science Oct Week 21 25 Mrs Bell S Blog 19




Sph4c
May 08, 21 · Gravitational potential energy may be converted to other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy If we release the mass, gravitational force will do an amount of work equal to mgh on it, thereby increasing its kinetic energy by that same amount (by the workenergyJul 01, 21 · In roller coasters, the two forms of energy that are most important are gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy Gravitational potential energy is the energy that an object has because of its height and is equal to the object's mass multiplied by its height multiplied by the gravitational constant (PE = mgh)Oct 05, 01 · Roller coasters have no engines Essentially a roller coaster is a gravitypowered train The movement of a roller coaster is accomplished by the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy The roller coaster cars gain potential energy as they are pulled to the top of the first hill As the cars descend the potential energy is converted




How Rollercoasters Work Science Of Rollercoasters



Stileapp Com Static Cll handouts Lesson 060 Handout Pdf
When riding a roller coaster, you go up and down many hills When do you have the maximum kinetic energy?Which of the following is an example of potential energy?




The Law Of Conservation Of Energy Life S A Roller Coaster Naturphilosophie




Roller Coasters Effort Motion Measures Of Who Likes




Paper Roller Coasters Kinetic And Potential Energy Lesson Plan
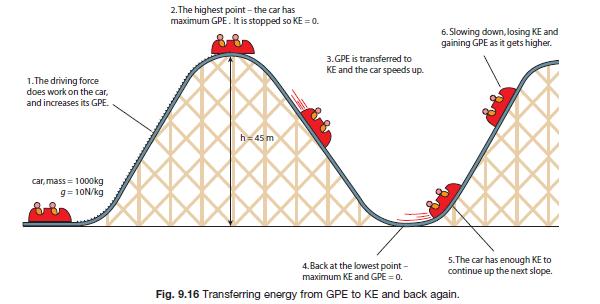



Slide 3
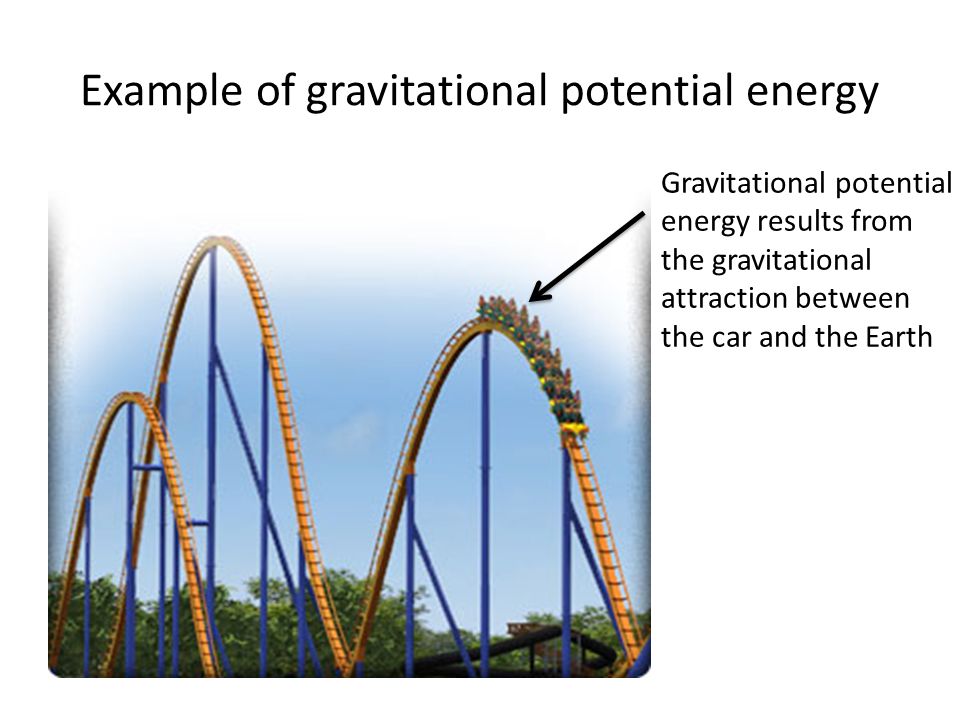



Forms And Transformation Of Energy Chapter 13 Sections 3 4 Pages Ppt Video Online Download



Search Q Kinetic Energy Formula Tbm Isch




Energy Forces And Motion Final Assessment Interactive Worksheet By Jenny Martin Wizer Me




15 Best Examples Of Potential Energy Rankred
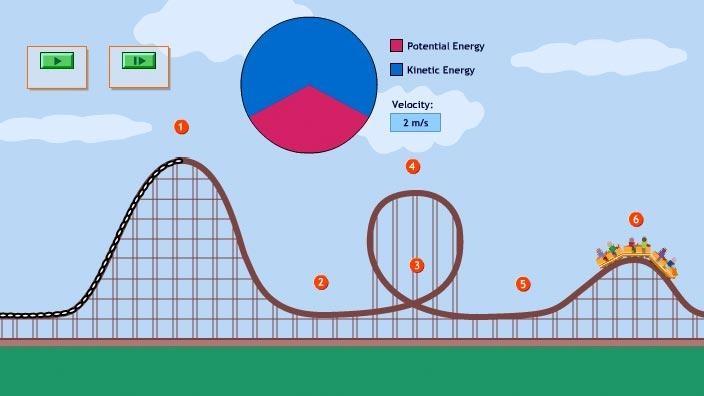



Energy In A Roller Coaster Ride Pbs Learningmedia



1



Www Romaisd Com Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 1991 Chapter 5 energy 7th science Pdf
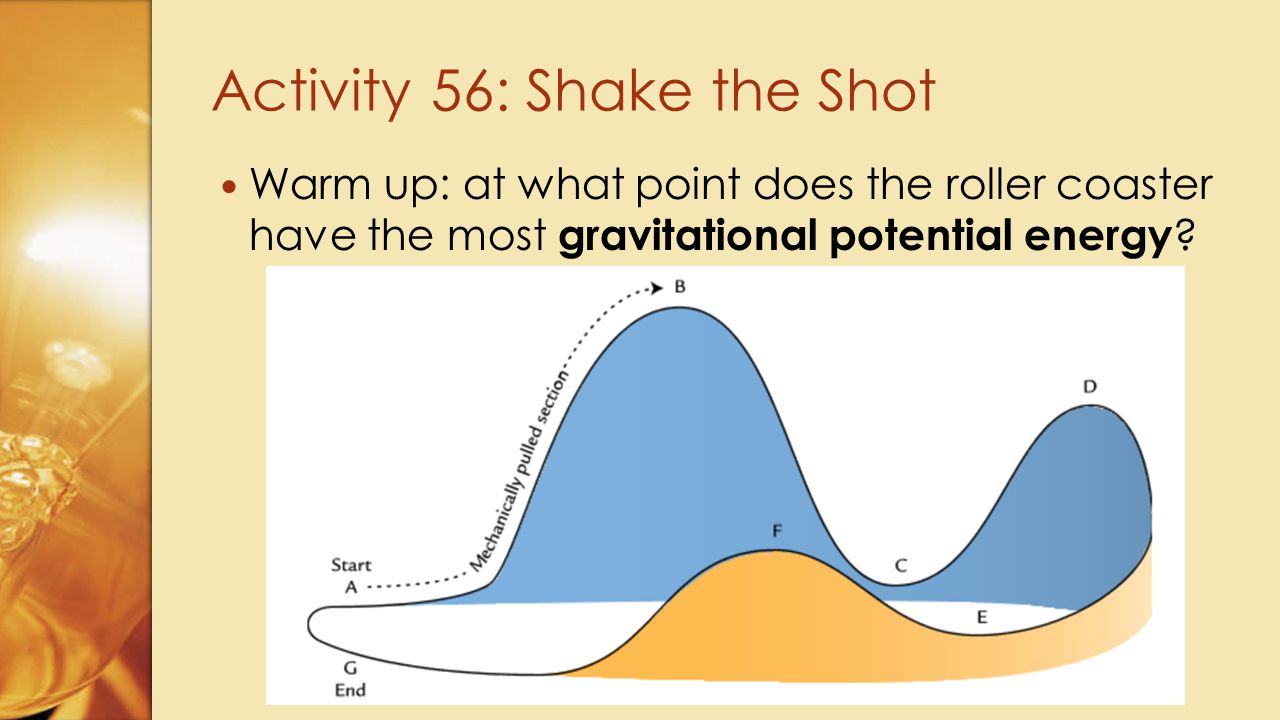



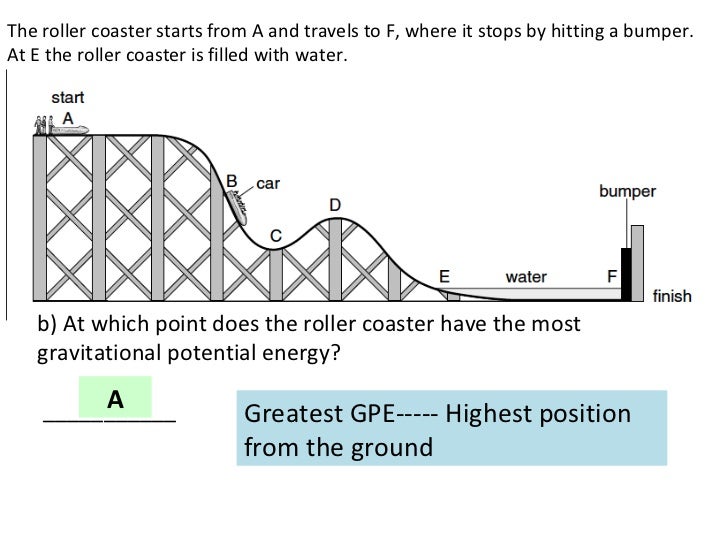
Warm Up At What Point Does The Roller Coaster Have The Most Gravitational Potential Energy Activity 56 Shake The Shot Ppt Download




Potential Kinetic Energy Transfer 6th Grade Flashcards Quizlet




Potential Energy Examples Integ Science 8 Jolley




Chapter 8 Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy
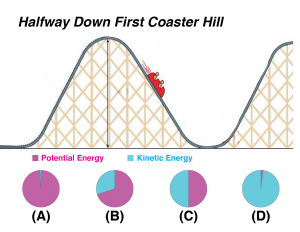



Potential And Kinetic Energy Chemistry Activities
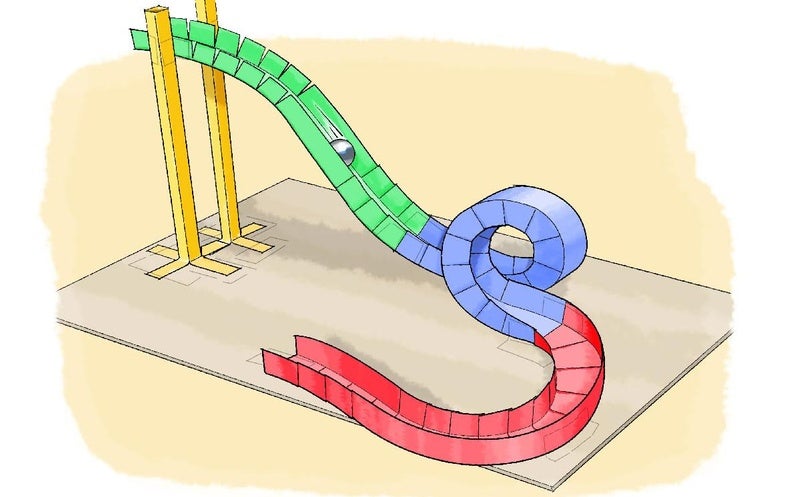



Paper Roller Coasters Scientific American




Potential And Kinetic Energy Review Flashcards Quizlet
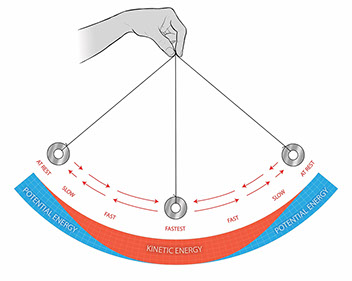



Lab Pendulum Energy



Flight Energy Transformations Gravitational Into Kinetic




Objective What Is The Difference Between Gravitational Elastic And Chemical Potential Energy What Is The Relationship Between Potential And Kinetic Ppt Download



Q Tbn And9gcrafefy3jl Oxipbbpqgr5txanp77t8w Sjgfnczxnintwi9klx Usqp Cau




Conservation Of Mechanical Energy Mechanical Energy Siyavula




1 Energy Is A Physical Quantity




Roller Coaster Energy Worksheets Teaching Resources Tpt




Potential Energy And Kinetic Energy Akshara Your True Exam Partner



Flight Energy Transformations Gravitational Into Kinetic



Potential Energy Vs Kinetic Energy Roller Coaster



Where Does A Roller Coaster Have The Most Kinetic Energy Quora




Paper Roller Coasters Kinetic And Potential Energy Lesson Plan



Potential And Kinetic Energy Energy Physics



Energy Ucanlearnthis Com



Roller Coaster Diagram Potential Kinetic Energy Data Diagram Medis




Roller Coaster Physics



Mechanical Energy How Are You A Scientist




At Least My Energy Has Potential Roller Coaster Physics




Roller Coaster Physics Study Com




Potential And Kinetic Energy Example Problem Work And Energy Examples




Physics 9 Conservation Of Energy 4 Of 11 Roller Coaster Youtube




Roller Coaster Physics Howstuffworks
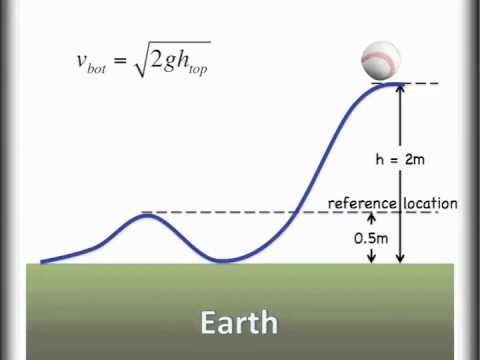



Potential And Kinetic Energy Exchange Conservation Of Energy Youtube
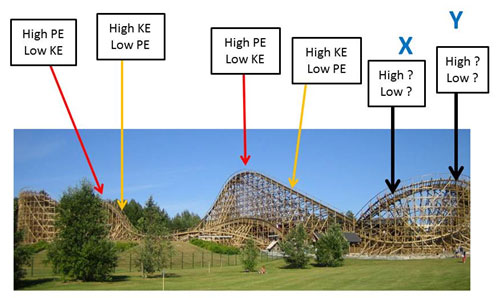



Kinetic And Potential Energy Texas Gateway
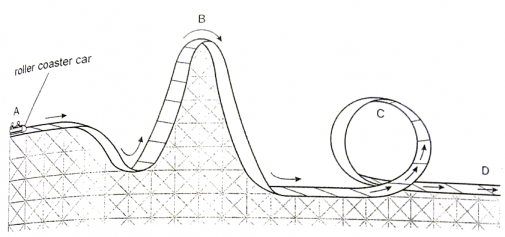



Gravity Force Energy And Acceleration Kiasuparents



Kastnerscienceamcms Weebly Com Uploads 3 7 4 5 Potential And Kinetic Energy 6 9a Pdf



Application And Practice Questions



Stileapp Com Static Cll handouts Lesson 060 Handout Pdf




Gravitational Potential Energy Ap Physics 1
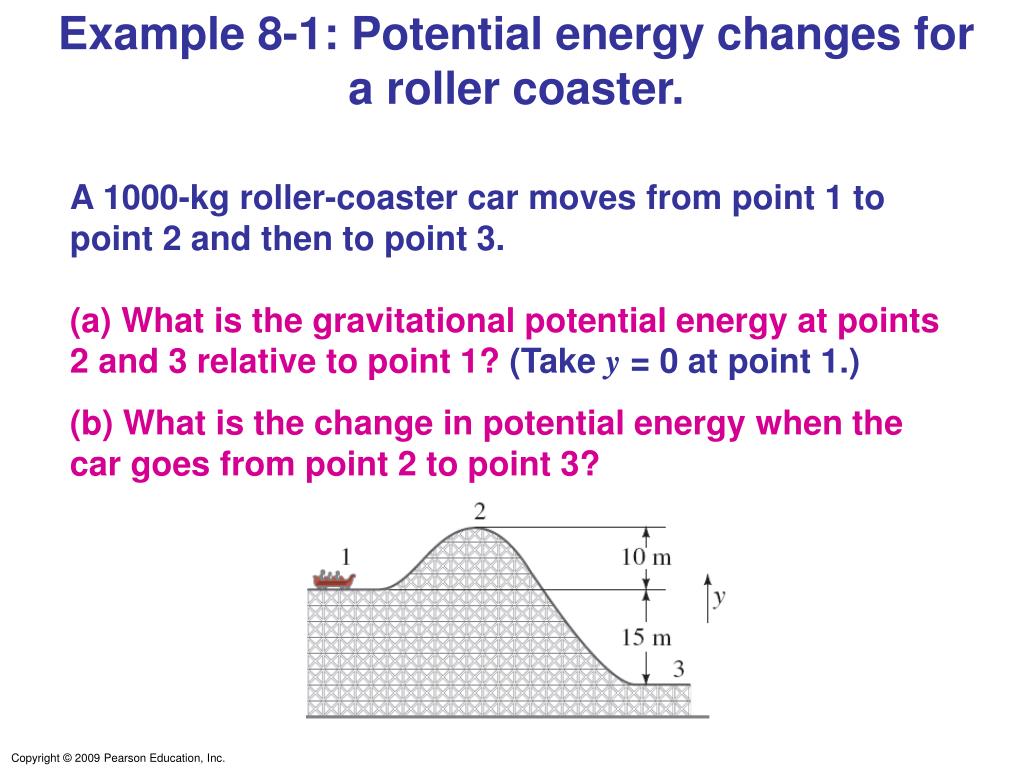



Ppt Chapter 8 Conservation Of Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Www Abss K12 Nc Us Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid Filename 43 unit 12 energy study guide answers Pdf




Physics Kinetic And Potential Energy In A Rollercoaster Youtube




Lesson 4 The Ups Downs Of Potential Kinetic Energy Energetic Connections




Speed Stopping Distance Of A Roller Coaster Physics University Of Wisconsin Green Bay
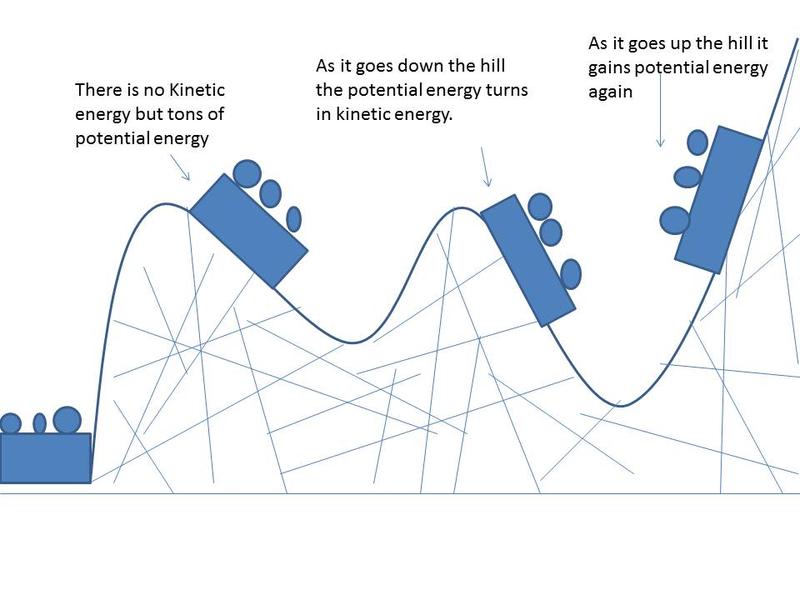



Roller Coasters Carly Badini



Worked Example 5 4 Roller Coaster Ride
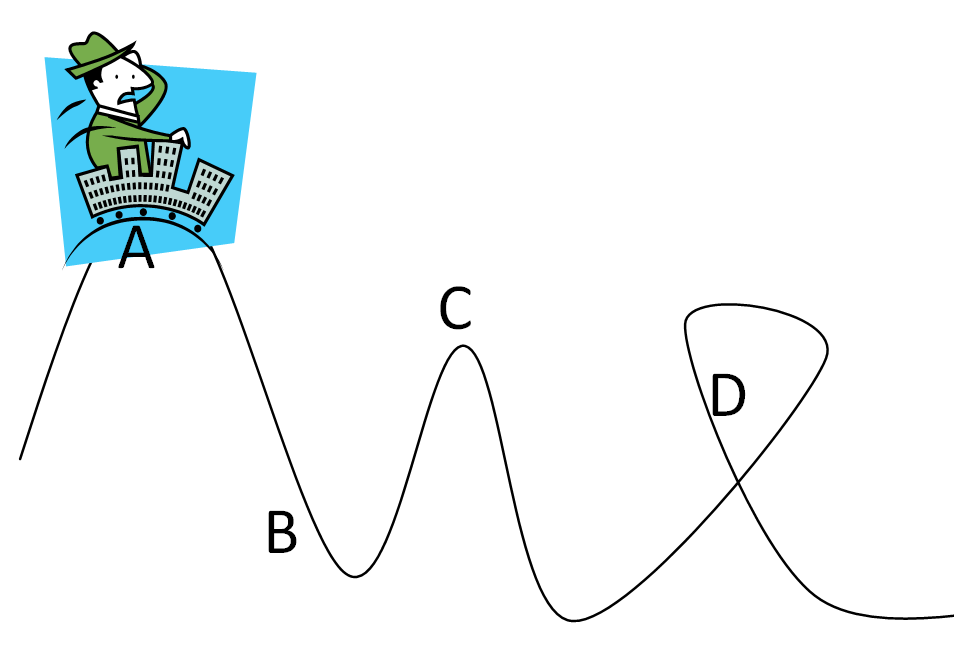



Kinetic Potential Energy Proprofs Quiz




Pin On Physics



1




11 Different Types Of Energy With Examples Rankred




Roller Coaster Physics




Study Guide For Science Standard 6 2 New




What Is Energy Energy Is The Ability To




Potential Energy And Kinetic Energy Akshara Your True Exam Partner




Physics Of Roller Coasters Lesson Teachengineering




Paper Roller Coasters Kinetic And Potential Energy Lesson Plan



The Scientific Theory Behind The Coasters Roller Coasters Usually Don T Have Engines Surprised Seems Hard To Believe But Most Of Them Travel Safely Around The Track Strictly By Using Gravity Friction And Speed How Does That Work It Converts Potential




Fisika Dasar Per 10




Ks3 Y9 Physics Potential And Kinetic Energy Teaching Resources




Kinetic And Potential Energy Ppt Download



The Physics Classroom Website



Potential And Kinetic Energy Roller Coaster Diagram
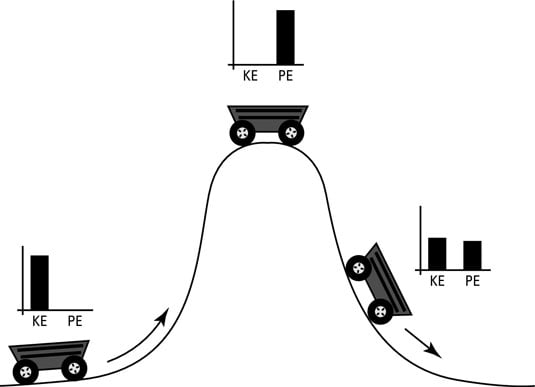



The Principle Of Conservation Of Mechanical Energy Dummies




Kinetic Energy




Where Is The Motor On A Roller Coaster Google Search




Kinetic Energy Wikipedia



Http Physics Gu Se Liseberg Eng Pe8 5 003 Pdf



Energy



Copy Of Roller Coasters A Study Of Energy Lessons Blendspace



Www Newpaltz K12 Ny Us Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 812 Energy roller coaster authentic assessment Pdf




Ppt Chapter 8 Conservation Of Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Http Www Sfu Ca Mxchen Phys P101lec09b Pdf


コメント
コメントを投稿